China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News. This statement, while bold, reflects the reality of China’s immense influence on global manufacturing. We’ll explore its historical ascent, examining key policies and strategies that propelled its growth, comparing its trajectory to other manufacturing giants. We’ll delve into specific sectors, highlighting successes and challenges, and analyzing its crucial role in global supply chains.
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking – a lot of those factories probably rely on robust software systems. If you’re a full-stack developer looking for some lucrative freelance work, check out this resource for opportunities and rates: full stack developer freelance opportunities and rates. It’s a good way to tap into that global supply chain, even indirectly! The demand for skilled developers supporting manufacturing is huge, especially in a country like China.
Finally, we’ll look at the future, considering technological advancements, potential obstacles, and the ongoing impact on global markets.
From its humble beginnings, China’s manufacturing sector has experienced explosive growth, fueled by strategic investments and a commitment to becoming a global powerhouse. This journey has involved both triumphs and setbacks, shaping not only its own economy but also the global economic landscape. Understanding this evolution is crucial for anyone interested in international trade, economics, or global supply chains.
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking – a lot of those devices are probably made with components from companies like Apple. Speaking of Apple, did you hear about the Apple Siri eavesdropping payout—Here’s who’s eligible and how ? It’s a reminder that even the biggest tech giants face scrutiny. The whole situation highlights the complex global supply chains powering our tech, many of which originate in China.
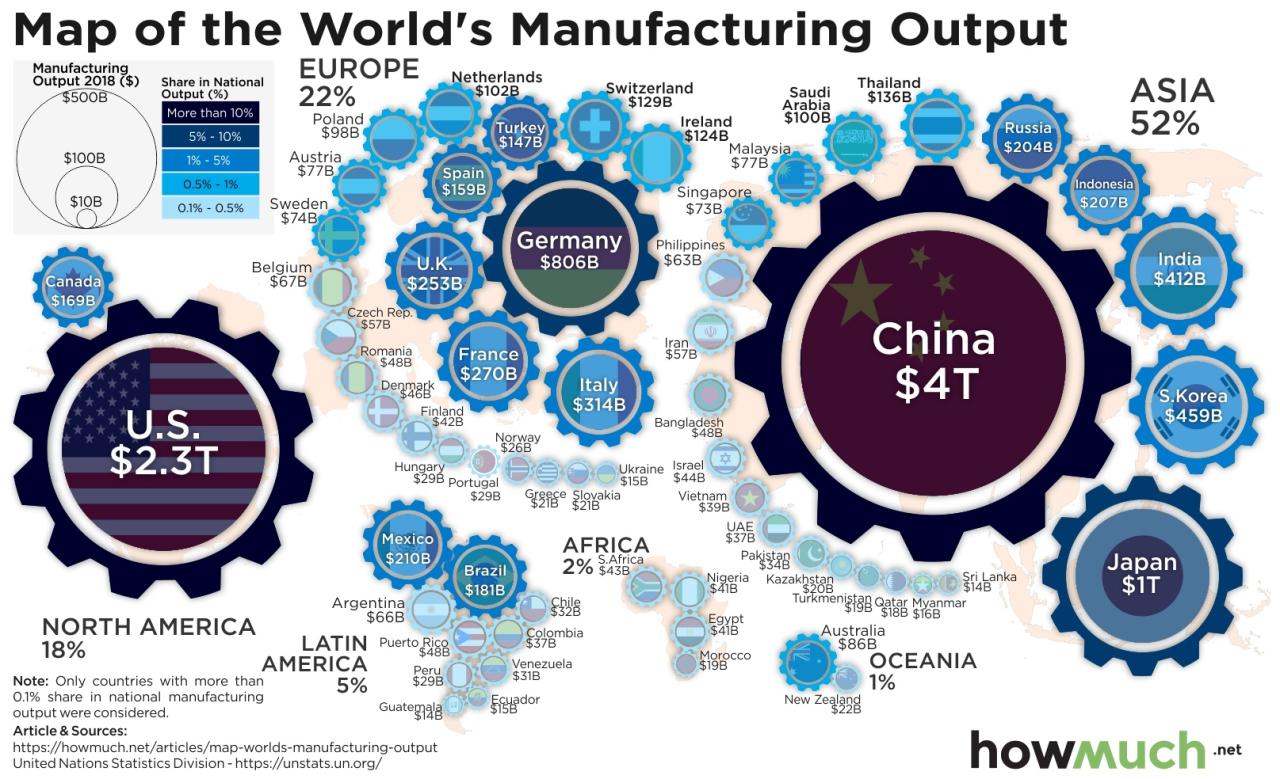
China’s Manufacturing Dominance: China Is The Manufacturing Superpower | Hacker News

China’s rise as the world’s manufacturing powerhouse is a remarkable story of economic transformation, driven by strategic policy decisions, massive investment, and a highly adaptable workforce. This ascent hasn’t been without its challenges, but its impact on global trade, economies, and consumer markets is undeniable. This article explores the key factors behind China’s manufacturing dominance, its current state, and the potential future of this industrial giant.
China’s Manufacturing Dominance: A Historical Perspective
China’s journey to manufacturing dominance began with significant economic reforms in the late 1970s, shifting from a centrally planned economy to a more market-oriented system. This opened the door for foreign investment and the rapid growth of export-oriented industries. Key policies like the establishment of Special Economic Zones (SEZs) attracted foreign capital and technology, fueling the expansion of manufacturing capabilities.
This strategic approach contrasts with the gradual, organic growth seen in earlier manufacturing powerhouses like the UK and the US, which built their industrial bases over centuries. Japan’s post-war “economic miracle” involved focused industrial policies and technological innovation, offering a closer parallel to China’s rapid ascent.
| Country | Manufacturing Output (USD Trillion, approx.) | Years of Dominance | Key Growth Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| United Kingdom | (Historical Data Varies) | 18th-19th Centuries | Industrial Revolution, Colonial Resources |
| United States | (Historical Data Varies) | Late 19th – Mid 20th Centuries | Mass Production, Technological Innovation, Abundant Resources |
| Japan | (Historical Data Varies) | Late 20th Century | Post-war Reconstruction, Technological Advancement, Export-Oriented Growth |
| China | Over 5 (approx.) | Early 21st Century – Present | Economic Reforms, Foreign Investment, Export-Oriented Strategy |
Key Sectors of Chinese Manufacturing
China’s manufacturing prowess spans a vast array of sectors. Some key areas include electronics, textiles and apparel, automobiles, machinery, and construction materials. While China excels in high-volume, low-cost manufacturing, it faces challenges in higher-value-added sectors that demand advanced technologies and innovation. Technological advancements are steadily improving, but the country is still striving for leadership in areas like semiconductors and high-end machinery.
- Electronics: Dominated by companies like Foxconn, assembling smartphones and other electronics for global brands. Strengths: massive scale, cost-effectiveness. Weaknesses: reliance on foreign technology in some key components.
- Textiles and Apparel: A historically significant sector, still a major exporter, but facing competition from lower-cost countries and automation. Strengths: established infrastructure, skilled workforce. Weaknesses: increasing labor costs, environmental concerns.
- Automobiles: Rapid growth in domestic brands like BYD and Geely, alongside foreign collaborations. Strengths: large domestic market, government support for electric vehicle development. Weaknesses: catching up in technology and brand recognition in certain segments.
Global Supply Chains and China’s Role, China is the manufacturing superpower | Hacker News

China’s integration into global supply chains is profound. It serves as a crucial manufacturing hub, producing components and finished goods for companies worldwide. This has led to lower prices for consumers globally, but also created dependencies and vulnerabilities. Disruptions to China’s manufacturing sector, whether due to natural disasters, geopolitical tensions, or pandemics, can have ripple effects across the globe, impacting production schedules, consumer prices, and overall economic growth.
Hypothetical Scenario: A prolonged shutdown of major Chinese ports due to a severe geopolitical event could significantly disrupt global supply chains, leading to shortages of various goods, increased prices, and potential economic recession in countries heavily reliant on Chinese imports.
Technological Advancements and Automation in Chinese Manufacturing
China is rapidly adopting automation and advanced technologies in its factories. While the level of automation might not yet match that of some leading nations like Germany or Japan in certain sectors, the pace of change is significant. This is driven by both government initiatives promoting technological upgrades and the need to address rising labor costs. However, this technological shift also has implications for employment, requiring retraining and adaptation of the workforce.
| Sector | Projected Employment Change (2023-2030) |
|---|---|
| Textiles | -15% (approx.) due to automation |
| Electronics Assembly | -10% (approx.) due to automation, but growth in related tech jobs |
| Robotics and Automation | +25% (approx.) significant job growth |
Challenges and Future Prospects for Chinese Manufacturing
China’s manufacturing sector faces several challenges. Rising labor costs, environmental concerns, and geopolitical tensions are significant headwinds. To maintain its global competitiveness, China needs to focus on innovation, technological advancement, and sustainable practices. A shift towards higher value-added manufacturing, focusing on research and development, and strengthening intellectual property protection are crucial.
That Hacker News thread about China’s manufacturing dominance got me thinking – how much of that production involves voiceovers? You’d need a seriously scalable solution, and that’s where a tool like this ai voice generator comes in handy. Imagine the efficiency boost for Chinese factories using AI for automated instructions and announcements; it could really accelerate their already impressive output.
- Scenario 1: China successfully transitions to a higher-value, technology-driven manufacturing base, maintaining its global leadership.
- Scenario 2: Geopolitical pressures and rising costs lead to a gradual decline in China’s manufacturing dominance, with production shifting to other regions.
The Impact of China’s Manufacturing on Global Markets
Chinese manufacturing has significantly impacted global markets, leading to lower prices for many goods. This has increased consumer purchasing power in many regions, particularly in developing countries. However, the impact has been uneven. Developed economies have seen increased competition and job losses in certain sectors, while developing economies have benefited from increased export opportunities and employment in manufacturing.
Illustrative Example: A Specific Chinese Manufacturing Company
Consider a hypothetical large-scale electronics manufacturer, “TechGiant Industries,” located in a sprawling complex in Shenzhen. Its vast factory floor is a highly organized system of automated assembly lines, robotic arms performing intricate tasks, and human workers specializing in quality control and advanced troubleshooting. The facility houses clean rooms for sensitive component assembly, expansive warehousing for raw materials and finished products, and sophisticated logistics systems to manage the flow of goods.
TechGiant’s success is built upon a combination of advanced technology, efficient processes, and a highly skilled workforce, allowing it to compete globally and supply major tech brands.
Final Summary

China’s dominance in manufacturing is undeniable, but its future isn’t guaranteed. While technological advancements and strategic planning offer pathways to continued success, challenges like rising labor costs, environmental concerns, and geopolitical shifts will require careful navigation. The long-term outlook hinges on China’s ability to adapt and innovate, ensuring its continued role as a key player in the global manufacturing landscape.
The story of China’s manufacturing superpower is far from over; it’s a dynamic narrative constantly evolving.
Essential Questionnaire
What are some examples of successful Chinese manufacturing companies?
Huawei (technology), Foxconn (electronics), BYD (automobiles), and many others are prominent examples, spanning various sectors.
How does China’s manufacturing impact developing economies?
It creates both opportunities and challenges. Lower prices for goods benefit consumers, but it can also impact local industries in developing nations through competition.
What are the environmental concerns related to Chinese manufacturing?
Rapid industrialization has led to significant pollution issues, prompting the government to implement stricter environmental regulations and invest in cleaner technologies.
What are the geopolitical risks associated with relying on Chinese manufacturing?
Geopolitical tensions and trade disputes can disrupt supply chains and create uncertainty for businesses reliant on Chinese production.
